3-ESS3-1,
4-ESS3-1,
5-ESS3-1,
3-LS4-4,
4-LS1-1,
5-PS3-1
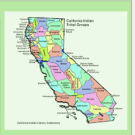
Through learning from California Native American perspectives, including voices from the Gabrieleno/Tongva tribe, students will explore how these values guide environmental stewardship and cultural practices. This lesson introduces students to core values within Indigenous knowledge systems, respect, reciprocity, and reverence, and their role in fostering sustainable relationships with the environment. The lesson encourages reflection on personal and collective responsibilities to the land and invites students to identify meaningful ways to honor and care for their local environment through everyday actions.